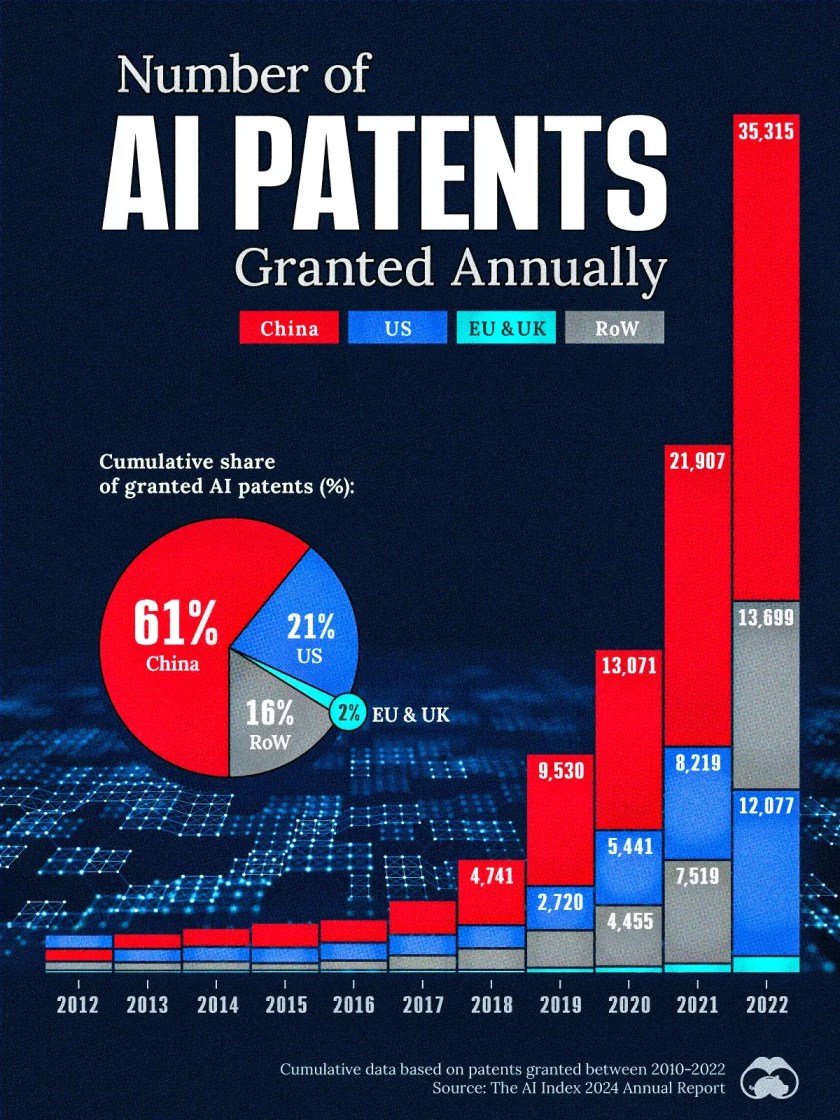
China’s share of granted artificial intelligence patents is 62%, approaching two-thirds worldwide. The U.S. comes in at 21% and the EU and UK just 2% – but these figures tell only part of the AI story.
The data from 2010 to 2022, the most recent available, are from a report released by Stanford University’s Center for Security and Emerging Technology, “2024 AI Index Report.”
China surpassed the U.S. in AI patents in 2013, according to CSET, and kept growing. These patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They are said to be more readily granted in China than the U.S. and Europe. Under the scrutiny of litigation many of these patents are likely to be found invalid.
“The number of new large language models released worldwide in 2023 doubled over the previous year. Two-thirds were open-source.”
In the U.S., AI patenting is largely concentrated among IBM, Microsoft, and Google. In China, AI patents are more distributed across tech firms (e.g. Baidu, Tencent), government organizations, and universities.
Because there is effectively no private ownership in China, the meaning of its patent leadership and ownership, as well has how the market share was achieved, is less clear.
It is not immediately clear from the report if it is referring to all patents filed globally (likely), those filed in the U.S. alone or those filed domestically by each region. If China’s patent grants are mostly domestic, their value will likely be more limited because of the difficulty enforcing them and winning significant damages.
Top Takeaways from the Stanford AI Report:
- AI beats humans on some tasks, but not on all.
- Industry continues to dominate frontier AI research.
- The United States leads China, the EU, and the U.K. as the leading source of top AI models.
- Generative AI investment skyrockets.
- The data is in: AI makes workers more productive and leads to higher quality work.
- People across the globe are more cognizant of AI’s potential impact—and more nervous.
The 2024 Index is CSET’s seventh. The introduction states the report “arrives at an important moment when AI’s influence on society has never been more pronounced. This year, we have broadened our scope to more extensively cover essential trends such as technical advancements in AI, public perceptions of the technology, and the geopolitical dynamics surrounding its development.”
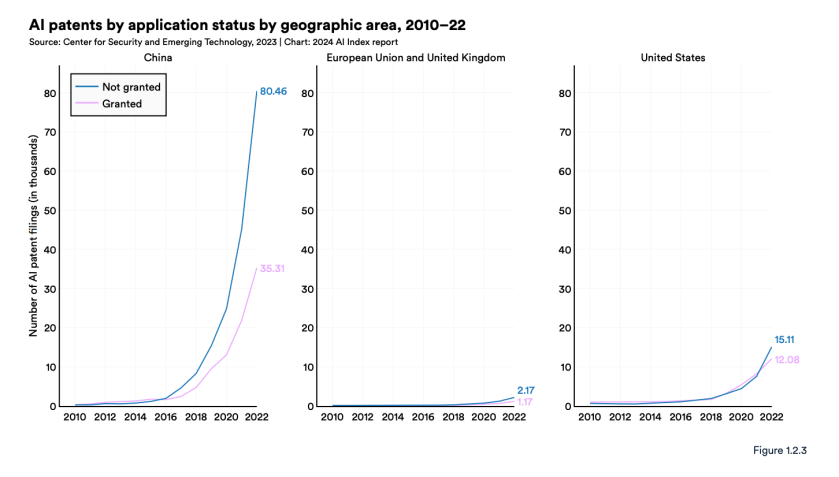
It appears from the graphs above that China is being more selective about the AI patents it grants than the U.S. and EU-UK. It would be interesting to know on what basis those rejections were make.
_______________________________
This year’s report introduces new estimates on AI training costs, detailed analyses of the responsible AI landscape, and an entirely new chapter dedicated to AI’s impact on science and medicine.
Two-Thirds are Open Source
“On the technical front,” said CSET co-directors Ray Perrault and Jack Clark, “this year’s AI Index reports that the number of new large language models released worldwide in 2023 doubled over the previous year. Two-thirds were open-source, but the highest-performing
models came from industry players with closed systems.”
Two of the five supporting partners of the Stanford report were Google and OpenAI. Analytics and Research Partners included GitHub and LinkedIn.
Go here full 500-page Stanford Human-Centered 2024 Artificial Intelligence report. It’s worth perusing.
Image source: VisualCapitalist; Center for Security and Emerging Technology